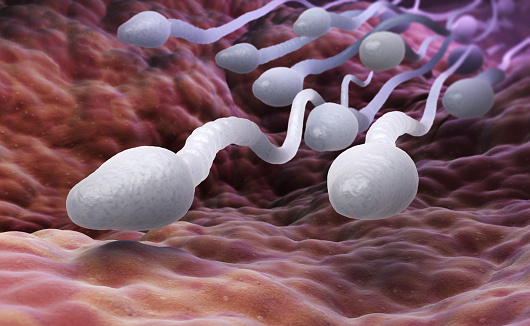
Sperm cell/ spermatozoa are the male reproductive cells that carry the genetic characters from the father to child. Sperms are formed in the pair of testis. Its main function is to reach the ovum and fuse to form an embryo. The pH of semen ranges from 7.2 to 7.8.
The normal spermatozoa consists of three main parts:
- Distinctive head
- Midpiece (body)
- Tail

HEAD OF SPERMATOZOA :
The head section also resembles an egg and has a smooth surface. The head is the most important part of the cell as it contains nucleus (genetic materials with 23 chromosomes ) require to form an new organism. It also possess a tiny secretary cap like structure called acrosome which is the product of Golgi complex. Once the sperm comes in contact with the egg , acrosome stimulates the cell to swim towards the egg. This recognition of egg based on molecule composition is known as chemotaxis and makes a physical contact in turn results in acrosome reaction.
MIDDLE PIECE:
The middle piece or neck is part of the sperm cell between head and the tail. The mid piece contains tightly packed mitochondrion that provides the energy to sperm to sustain motion.
The centriole is part of semen located between the head and the midpiece. The centriole is involved in the production of mitotic apparatus involved in separating chromosome during cell division.
TAIL OF SPERMATOZOA:
The sperm tail is a thin, elongated structure that creates up to 80 percent of the whole length of the sperm. The tail provides the capability to pass through the vaginal cavity towards the egg. It is divided into several parts includes:
- Connecting piece- part that connects the flagellum to the sperm head
- Principal piece – (axial filament )
- End piece – generates the waveform that allow for movement.
Several components including sperm cells, enzymes, sugars, and vitamin compose semen. Four glands contribute their secretions to the seminal fluid- testes, seminal vesicles, prostate and bulbourethral gland.
EXAMINATION OF SPERMATOZOA
Semen as evidence is involved in heinous crime such as rape, murders, child abuse, incest and unnatural offences. The quantity of seminal fluid in a single emission is 2-5 ml and contains about 60-150 millions of sperms per ml. Semen contain lipids, fructose, proteins and a number of enzymes. Prostate secretes mainly acid phophatase, spermine and zinc, while seminal vesicles secrete choline which helps in identification of seminal fluid.
Semen, like other physical evidence in offences against the person, including sexual assaults helps to:
- Establish corpus delicti.
- Identify the culprit/ victim.
- Eliminate the innocent suspect/ accused.
ENZYME TYPING: PGM and peep A found in semen and vaginal secretions are two enzyme markers commonly used in genetic profiling of semen.
- VISUAL AND PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
COLOR: thick, yellowish, white, gray secretion having a characteristic odor known as seminal odor.
TEXTURE: on touch, seminal stains are starchy and on drying they have characteristic rough and brittle nature.
EXAMINATION THROUGH UV LIGHT: Semen show a fluorescence of a bluish-white color (due to choline) when examined under UV light.
MICROSCOPIC EXAMINATION: microscopically, detection of spermatozoa is also considered as confirmatory evidence for the presence of semen in a suspected stain. In order to conduct microscopic identification, a part of stained garment should be dissolved in acidulated water in test tube. The tube should be subjected to ultra sonic oscillation, which may separate the spermatozoa from the dried stain, followed by microscopic examination after fixing the same in dilute sulphuric acid. Spermatozoa contain gram positive protein, the presence of spermatozoa are going to be confirmed by purple microscopic bodies. Human spermatozoa vary from 50-55 microns in length and consist of head, neck and tail.

2. PRESUMPTIVE TEST:
ACID PHOSPHATE TEST: the acid phosphate test is one of the most widely technique for the purpose of identification of semen. This test is adopted due to high acid phosphatase activity of semen.
REAGANT:
Sodium alpha-napthyl phosphate
Naphthanil diazo blue B, 0.5% (w/v)
PROCEDURE:
- Stain material on whatmann filter paper or other suitable filter paper. Use proper standards and controls including positive, negative and unstained controlled.
- Add 1-2 drops of sodium alpha-napthyl phosphate reagent and allow to reacting for 30 seconds.
- Add 1 drop of napthanil diazo blue B reagent. Record the result after 10 seconds.
- A positive reaction is recorded upon rapid development of a purple color, which is an indicative of semen.
3. CONFIRMATORY TESTS
FLORENCE TEST: this test was discovered by Dr. Florence in the year 1886. The stain is extracted by 1 ml hydrochloric acid, and a drop is placed on a glass slide and allowed to dry. A cover slip is placed over this, and a drop of Florence solution (potassium iodide, iodine and water) is allowed to run under the cover slip. Is semen is present, dark – brown rhombic or needle shaped crystals of choline iodide appear immediately. Any tissue or biological material containing sufficient choline concentration would give positive Florence test.
BARBERIO’S TEST: this test was invented by barberio in the year of 1905. When the questioned stain is allowed to react with picric acid and results in the formation of yellow needle shaped spermine picrate crystals, including the presence of seminal stain.
THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY
Liquid and dried seminal stains often be identified by a thin layer chromatography technique. The test is based on unique combination of choline and spermine which is present only in semen. Spermine is found in testes, pancreas, liver, spleen but its concentration is lower than in semen. One microlitre of semen present can be detected by this method. After vasectomy, chemical and enzymatic tests for semen remains positive, though no sperm will be present.
PROTEIN CONFIRMATION OF SEMEN: prostate specific antigen (PSA, P30) is a glycoprotein produced by prostate and is found in seminal plasma. It is found in vaginal fluid up to 27 hrs after sexual intercourse, but sometimes may be detected up to 47 hrs. The binding of P30 to the antibody confirms the presence of seen in stain. A positive PSA finding is a reliable measure of semen, regardless of the presence of spermatozoa or elevated acid phosphatase level.
subscribe to our blog for more updates.